Overview
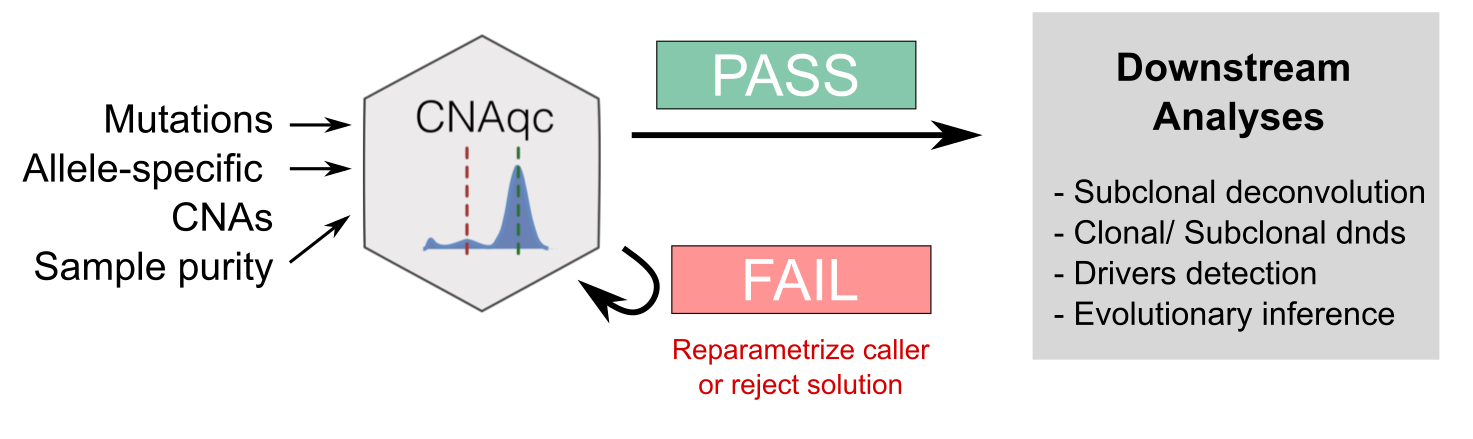
CNAqc Input/Output
Summary
CNAqc requires in input
- read counts from somatic mutations such as single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) or insertion-deletions (indels);
- allele-specific copy number segments (CNAs) for clonal segments and, optionally, for subclonal segments;
- a tumor purity estimate.
CNAqc uses chromosome coordinates the to map mutations to segments. The conversion of relative to absolute genome coordinates requires to fix a reference genome build; supported references are GRCh38/hg17 and hg19/GRCh37, but custom references can also be built.
The tool can elaborate a number of analysis to assess the consistency among mutations, CNAs and tumour purity (see Articles).
CNAqc can be used to:
- QC concordance across the input mutations, CNAs and purity;
- select among alternative tumour segmentations and purity/ ploidy estimates;
- optimize CNA calling with automatic QC procedures leveraging the Sequenza copy number caller;
- estimate CCF values of the input variants, and estimate their uncertainty;
- identify patterns of over-fragmentation of chromosome arms;
- smooth and subset segments with various filters;
- annotate putative driver mutations among the input variants, using VariantAnnotation.
The model
The following concepts are used to develop CNAqc.
VAF peaks
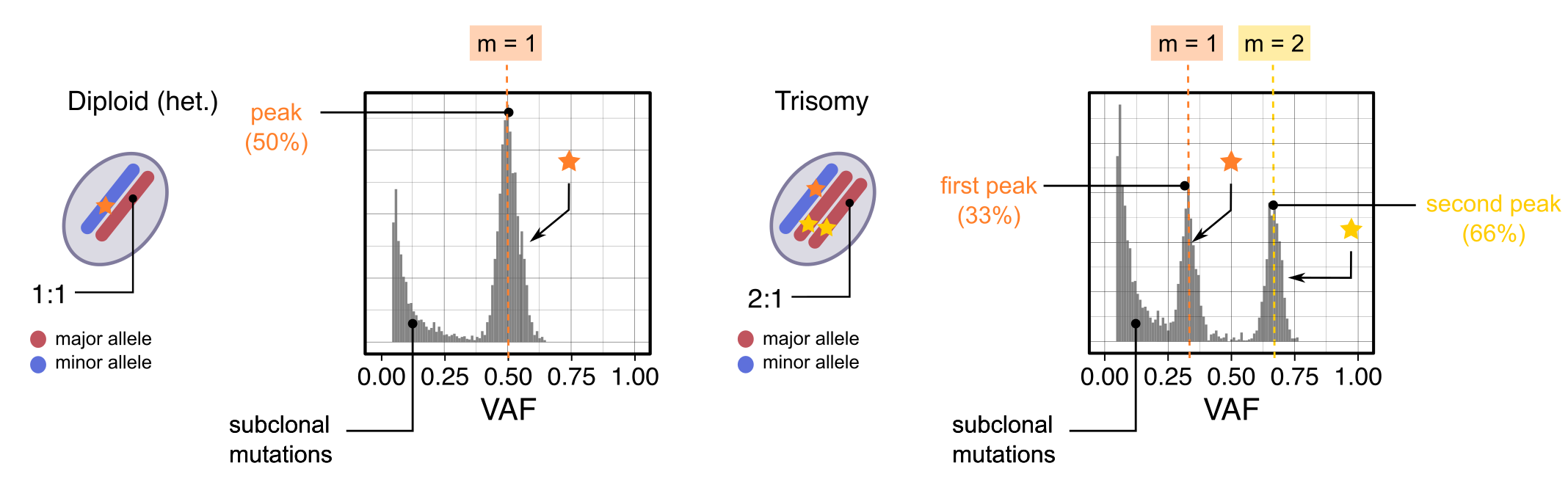
Expected VAF peaks for mutations mapped to diploid heterozygous and
triploid clonal CNAs (at purity
).
Clonal CNAs
Consider:
- mutations present in a percentage of tumour cells, sitting on a segment ;
- tumour purity ;
- a healthy diploid normal;
Since the proportion of all reads from the tumour is , and from the normal is . Then, muations present in copies of the tumour genome should peak at VAF value