Construct a `ctree` clone tree computing its structure.
ctrees.RdThis constructor creates a list of objects of class `'ctree'`, after using a sampling strategy to determine possible trees that fit the data. The strategy to sample trees can be controlled, a maximum number of trees can be sampled with a Monte Carlo procedure and the actual process can be exhausted if there are less than a number of available trees to fit the data.
Note that the parameters of this function includes the same parmeters of
function ctree, plus the parameters of the sampler. See
ctree for an explanation of the parameters.
Usage
ctrees(
CCF_clusters,
drivers,
samples,
patient,
sspace.cutoff = 10000,
n.sampling = 5000,
store.max = 100
)Arguments
- CCF_clusters
Clusters of Cancer Cell Fractions available in the data of this patient. See the package vignette to see the format in which this should be specified.
- drivers
A list of driver events that should be annotated to each one of the input clusters contained in the `CCF_clusters` parameter. See the package vignette to see the format in which this should be specified.
- samples
A vector of samples names (e.g., the biopsies sequenced for this patient).
- patient
A string id that represent this patient.
- sspace.cutoff
If there are less than this number of tree available, all the structures are examined in an exhaustive fashion. Otherwise, if there are more than this, a Monte Carlo sampler is used.
- n.sampling
If a Monte Carlo sampler is used,
n.samplingdistinct trees are sampled and scored.- store.max
When a number of trees are generated, scored and ranked, a maximum of
store.maxare returned to the user (these are selected following the ranking).
Value
An list of objects of class "ctree" that represent the trees that
can be fit to the data of this patient..
Examples
data('ctree_input')
x = ctrees(
ctree_input$CCF_clusters,
ctree_input$drivers,
ctree_input$samples,
ctree_input$patient,
ctree_input$sspace.cutoff,
ctree_input$n.sampling,
ctree_input$store.max
)
#> [ ctree ~ clone trees generator for CUK12345 ]
#>
#> # A tibble: 7 × 7
#> cluster nMuts is.driver is.clonal R1 R2 R3
#> <chr> <int> <lgl> <lgl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 72 TRUE FALSE 0 0.92 0
#> 2 2 69 TRUE TRUE 0.99 0.98 0.99
#> 3 3 48 FALSE FALSE 0 0 0.49
#> 4 4 29 FALSE FALSE 0.01 0.01 0.93
#> 5 5 24 TRUE FALSE 0.78 0 0
#> 6 6 23 TRUE FALSE 0.98 0.03 0.98
#> 7 7 15 FALSE FALSE 0 0.41 0
#>
#> ✔ Trees per region 1, 3, 1
#> ℹ Total 3 tree structures - search is exahustive
#>
#> ── Ranking trees
#> ✔ 3 trees with non-zero score, storing 3
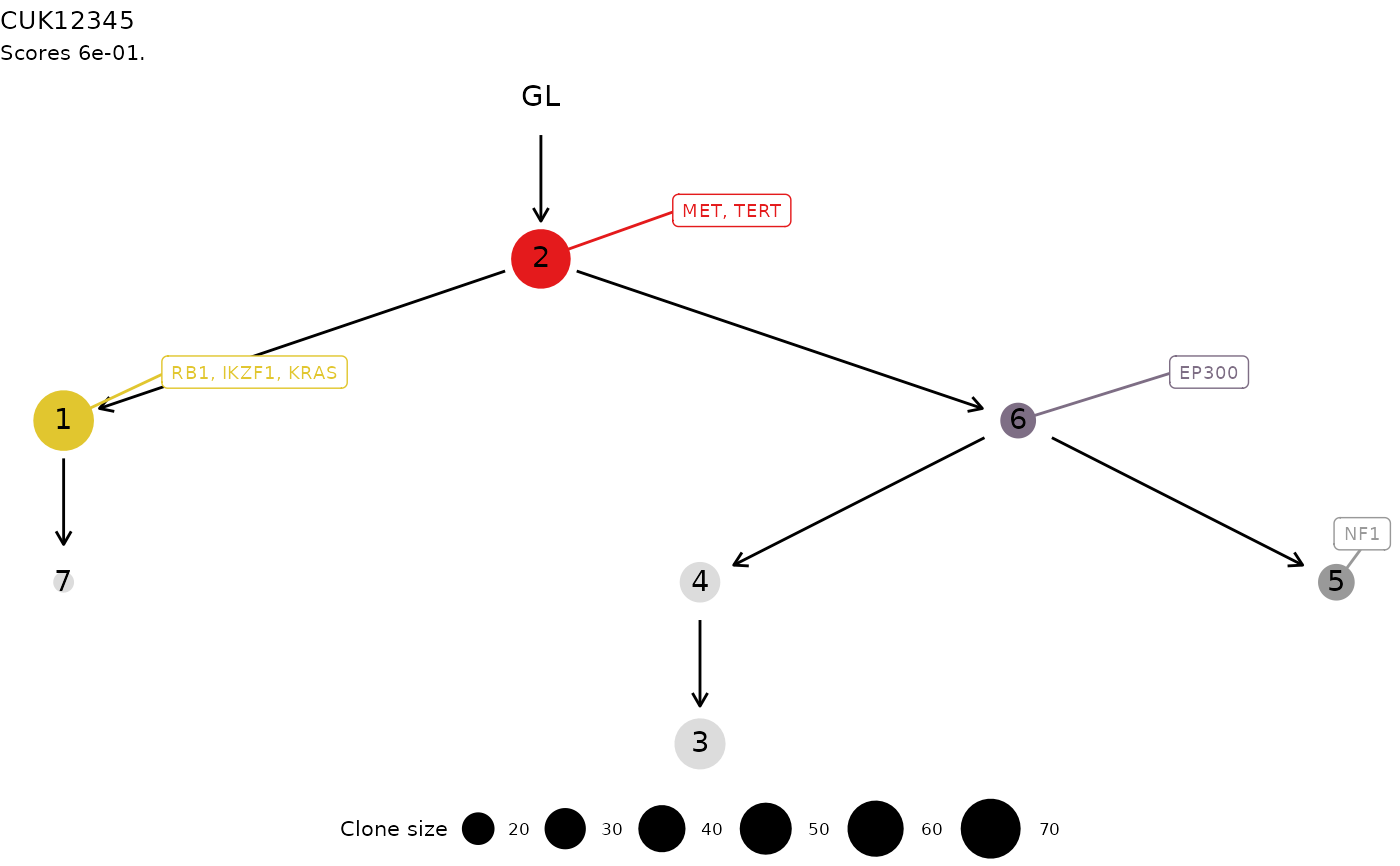
print(x[[1]])
#> [ ctree - ctree rank 1/3 for CUK12345 ]
#>
#> # A tibble: 7 × 7
#> cluster nMuts is.driver is.clonal R1 R2 R3
#> <chr> <int> <lgl> <lgl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 72 TRUE FALSE 0 0.92 0
#> 2 2 69 TRUE TRUE 0.99 0.98 0.99
#> 3 3 48 FALSE FALSE 0 0 0.49
#> 4 4 29 FALSE FALSE 0.01 0.01 0.93
#> 5 5 24 TRUE FALSE 0.78 0 0
#> 6 6 23 TRUE FALSE 0.98 0.03 0.98
#> 7 7 15 FALSE FALSE 0 0.41 0
#>
#> Tree shape (drivers annotated)
#>
#> \-GL
#> \-2 :: MET, TERT
#> |-1 :: RB1, IKZF1, KRAS
#> | \-7
#> \-6 :: EP300
#> |-4
#> | \-3
#> \-5 :: NF1
#>
#> Information transfer
#>
#> MET ---> RB1
#> MET ---> IKZF1
#> MET ---> KRAS
#> TERT ---> RB1
#> TERT ---> IKZF1
#> TERT ---> KRAS
#> GL ---> MET
#> GL ---> TERT
#> EP300 ---> NF1
#> MET ---> EP300
#> TERT ---> EP300
#>
#> Tree score 0.6
#>
plot(x[[1]])
#> Warning: Duplicated aesthetics after name standardisation: na.rm
#> Warning: `guides(<scale> = FALSE)` is deprecated. Please use `guides(<scale> = "none")` instead.
#> Warning: Removed 1 rows containing missing values (geom_point).